November 18, 2024
How Tumor Location Shapes Symptoms
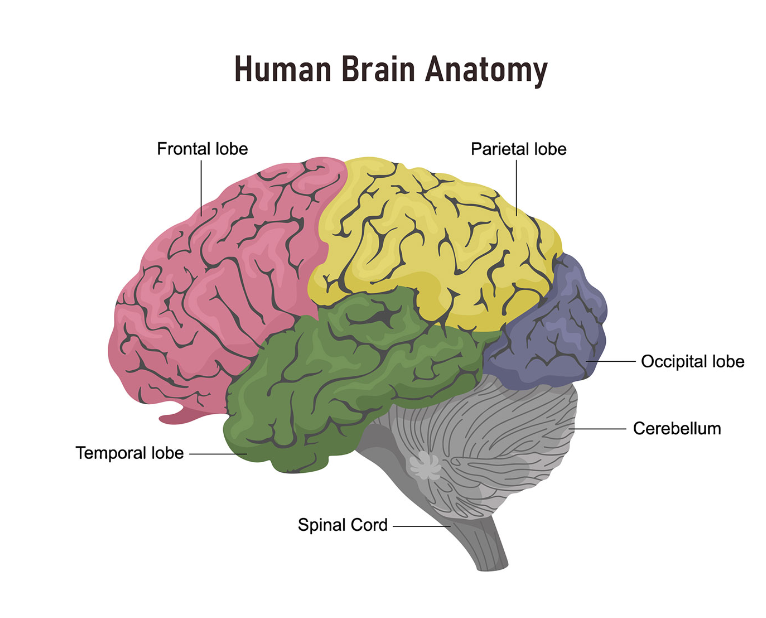
Imagine your brain is like a busy city, with different neighborhoods responsible for different tasks. Just like how each part of a city plays a unique role in keeping things running smoothly, each area of your brain has important functions too. When a tumor moves in, it’s like a disruptive visitor causing chaos in a specific neighborhood, leading to various challenges. To better understand these effects, let’s take a closer look at each lobe and the role it plays in the brain’s overall function.
- Frontal Lobe – The “Control Center”: The frontal lobe can be compared to the boss of the brain, managing movements, speech, and decision-making. If a tumor sets up camp here, it’s like the boss taking an unexpected leave, causing confusion in the workplace – you might find it hard to focus, remember things, or control your actions. Personality changes, such as becoming irritable or impulsive, and difficulties with planning and organizing tasks are also common.
- Parietal Lobe – The “Feeling Center”: Think of the parietal lobe as your brain’s GPS, helping you sense touch, pain, and where your body is in relation to things around you. If a tumor moves in, it’s like your GPS getting scrambled – you might feel lost in your own body, struggle to coordinate movements, or have trouble understanding words and numbers. You may also experience difficulties with hand-eye coordination, balance, and interpreting sensations.
- Temporal Lobe – The “Memory Bank”: The temporal lobe acts as your brain’s librarian, storing memories, helping you hear and understand language, and managing emotions. When a tumor affects this area, it’s like the librarian misplacing important books – you might struggle to remember things, recognize faces, or control your emotions. You could also experience changes in hearing, mood swings, or even seizures.
- Occipital Lobe – The “Visual HQ”: Picture the occipital lobe as your brain’s art studio, processing colors, shapes, and visual information. If a tumor intrudes here, it’s like your studio getting dimmed – you might have trouble seeing clearly, recognizing faces, or judging distances. Visual perception may also become distorted, causing confusion when interpreting what you see.
- Cerebellum – The “Balance Keeper”: Consider the cerebellum as the brain’s choreographer, orchestrating balance and coordination. Should a tumor disrupt this area, it’s like the choreographer losing their rhythm – you might find it hard to walk steadily, control your muscles, or speak clearly. Tasks requiring precise movements, like buttoning a shirt, may become difficult.
- Brainstem– The “Life Support System”: Located above the spinal cord at the base of the brain, the brainstem is like the brain’s emergency room, regulating vital functions like breathing, heartbeat, and sleep patterns. If a tumor invades here, it’s like a blackout in the emergency room – you might struggle to breathe, stay awake, or maintain balance. Other possible effects include changes in facial movements, speech difficulties, and trouble swallowing.
While brain tumors can disrupt life’s harmony, understanding how their location shapes symptoms can help make this complex topic more manageable. Just like a map guides you through a maze, knowledge of the brain’s regions can help you navigate the challenges of facing a brain tumor diagnosis.
References
Cleveland Clinic. (2021, June 21). Brainstem: Overview, Function & Anatomy. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21598-brainstem
Cleveland Clinic. (2022a, July 7). Cerebellum: What It Is, Function & Anatomy. Cleveland Clinic; Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23418-cerebellum
Cleveland Clinic. (2022b, December 5). Frontal lobe: What it is, function, location & damage. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/24501-frontal-lobe
Cleveland Clinic. (2022c, December 5). Occipital Lobe: Function, Location & Conditions. Cleveland Clinic; Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/24498-occipital-lobe
Cleveland Clinic. (2023a, January 8). Parietal Lobe: What It Is, Function, Location & Damage. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/24628-parietal-lobe
Cleveland Clinic. (2023b, January 8). Temporal Lobe: What It Is, Function, Location & Damage. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/16799-temporal-lobeJohn Hopkins Medicine. (2024). Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works. Johns Hopkins Medicine; Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/anatomy-of-the-brain